library(readxl)
library(tidyverse)
# declare where you are in your project folder
i_am("practice1.R")
# construct the path to your data
path <- here("data", "ecommerce.xlsx")
# read the two sheets by specifying the "sheet" argument
purchases <- read_xlsx(path = path, sheet = "purchases_history")
products <- read_xlsx(path = path, sheet = "products")Solutions Lab 4 practice
Practice 1
For importing, use the read_xlsx()function and specify the sheet argument.
Exercise 1
library(janitor)
purchases <- purchases |> clean_names()
products <- products |> clean_names()To compute the total number of sales by product we can use the group_by() + summarise() combo.
purchases |>
group_by(product) |>
summarise(
number_of_sales = n()
)# A tibble: 7 × 2
product number_of_sales
<chr> <int>
1 e-reader 96
2 earphones 115
3 laptop_1 48
4 laptop_2 46
5 smartphone_1 49
6 smartphone_2 52
7 tablet 94There is even a faster way to count how many times the values of a given variable appear in the dataset. Literally, you can pipe the count() function
purchases |>
count(product)# A tibble: 7 × 2
product n
<chr> <int>
1 e-reader 96
2 earphones 115
3 laptop_1 48
4 laptop_2 46
5 smartphone_1 49
6 smartphone_2 52
7 tablet 94Exercise 2
To compute the total amount of money spent on each product we first join the two datasets,
purchases |>
left_join(products, by = "product") # A tibble: 500 × 3
customer_id product price_euro
<chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 1609fdd7-29c6-4678-84af-30684d709f0b earphones 90.0
2 1064a4dc-df76-4aba-8b74-953a4c66fa16 smartphone_1 500.
3 155e9331-3434-415f-9d66-67736534d80b e-reader 200.
4 105696b8-7c38-4fe5-92f5-3c6fb1268f48 laptop_2 900.
5 12175814-556e-4e1a-af05-0c38c13e98a0 laptop_1 2140.
6 80fb4c6d-d5f8-42ed-b3c7-8a10596dd382 tablet 520.
7 348651a5-8a5a-4311-b999-4dfba846a413 e-reader 200.
8 cea15e94-869f-417a-9ad4-a70aefc74f34 laptop_2 900.
9 8b0a0720-0487-44d2-9aae-32dfec5c4b5c e-reader 200.
10 578ffa9d-ec4c-4a54-8a32-6f15ac4deb53 e-reader 200.
# ℹ 490 more rowsand then comput the totals,
purchases |>
left_join(products, by = "product") |>
group_by(product) |>
summarise(
total = sum(price_euro),
total_thousands = sum(price_euro)/1000
)# A tibble: 7 × 3
product total total_thousands
<chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 e-reader 19199. 19.2
2 earphones 10349. 10.3
3 laptop_1 102720. 103.
4 laptop_2 41400. 41.4
5 smartphone_1 24500. 24.5
6 smartphone_2 15599. 15.6
7 tablet 48879. 48.9Equivalently, we can also first count how many items have been sold by product type, as in the previous exercise, and then join the resulting table with the price listings
purchases |>
count(product) |>
left_join(products)# A tibble: 7 × 3
product n price_euro
<chr> <int> <dbl>
1 e-reader 96 200.
2 earphones 115 90.0
3 laptop_1 48 2140.
4 laptop_2 46 900.
5 smartphone_1 49 500.
6 smartphone_2 52 300.
7 tablet 94 520. Once here, we need to compute total by product by multiplying their prices and quantities sold
purchases |>
count(product) |>
left_join(products) |>
mutate(
total_thousands = price_euro * n /1000
)# A tibble: 7 × 4
product n price_euro total_thousands
<chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
1 e-reader 96 200. 19.2
2 earphones 115 90.0 10.3
3 laptop_1 48 2140. 103.
4 laptop_2 46 900. 41.4
5 smartphone_1 49 500. 24.5
6 smartphone_2 52 300. 15.6
7 tablet 94 520. 48.9Practice 2
Exercise 1
library(readxl)
library(tidyverse)
# declare where you are in your project folder
i_am("practice2.R")
# construct the path to your data
path <- here("data", "avocados.xlsx")
avocados <- read_xlsx(path = path)We need to use pivot_longer() to reshape the data:
new_avo <- avocados |>
pivot_longer(
cols = c(conventional, organic),
names_to = "type",
values_to = "avg_price"
)
new_avo# A tibble: 338 × 3
date type avg_price
<dttm> <chr> <dbl>
1 2015-01-04 00:00:00 conventional 1.01
2 2015-01-04 00:00:00 organic 1.59
3 2015-01-11 00:00:00 conventional 1.11
4 2015-01-11 00:00:00 organic 1.63
5 2015-01-18 00:00:00 conventional 1.13
6 2015-01-18 00:00:00 organic 1.65
7 2015-01-25 00:00:00 conventional 1.12
8 2015-01-25 00:00:00 organic 1.68
9 2015-02-01 00:00:00 conventional 0.962
10 2015-02-01 00:00:00 organic 1.53
# ℹ 328 more rowsOnce reshaped, we can plot the price trajectories over time:
new_avo |>
ggplot(aes(x=date, y=avg_price, col=type))+
geom_line()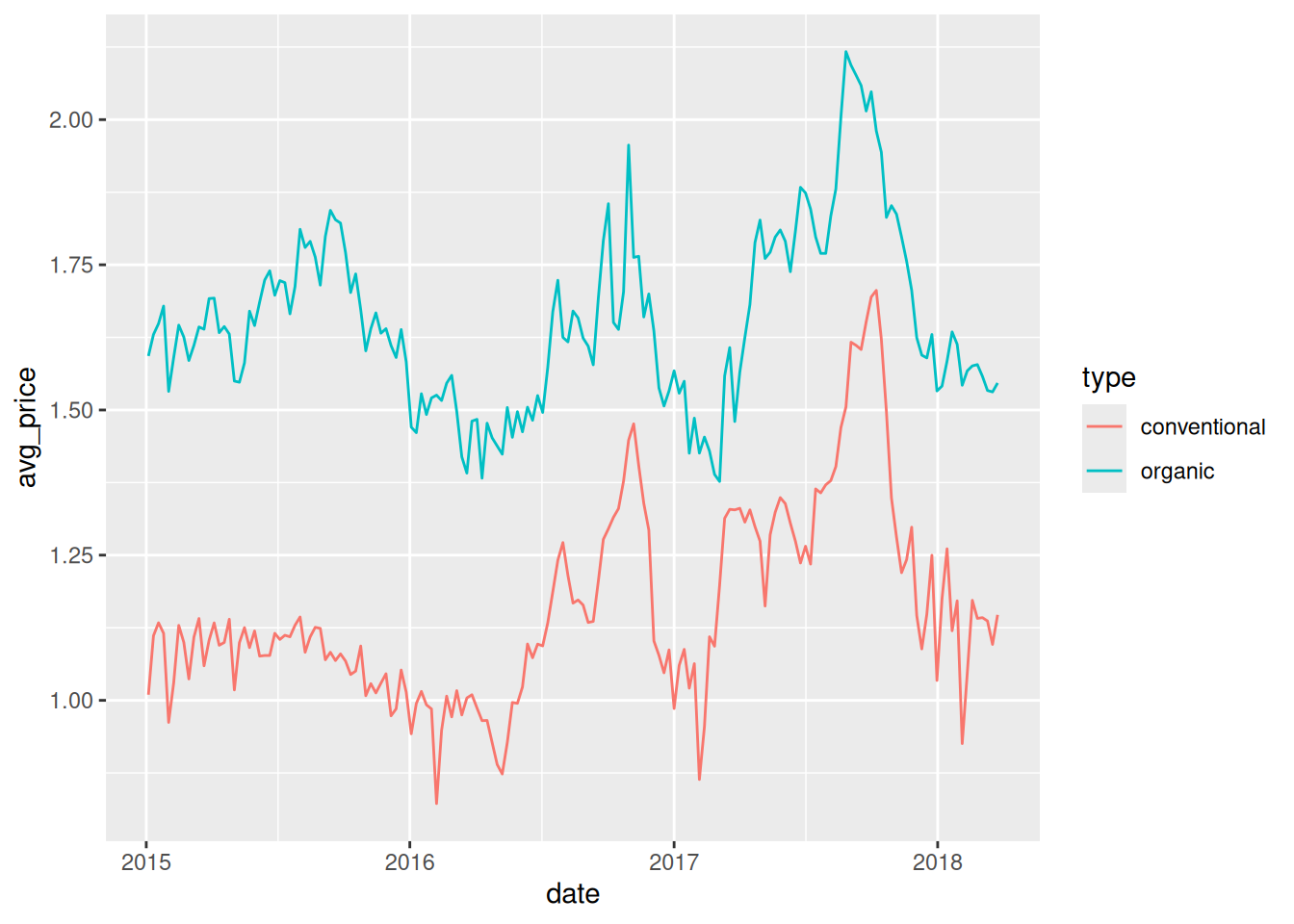
As always, we can customise the plots as we prefer:
library(ggokabeito)
new_avo |>
ggplot(aes(x=date, y=avg_price, col=type))+
geom_line(linewidth=1) +
labs(x="", y= "Average price ($)", color="Avocado origin:")+
theme_bw() +
theme(
legend.position = "top",
panel.grid.minor = element_blank()
)+
scale_color_okabe_ito()